
Namely, the Binance Smart Chain has only 21 validating nodes in its PoSA network, compared to Ethereum, which has about 10,000 PoW mining nodes. That being said, Binance’s flagship smart contract platform for “decentralized” applications is a bit of an oxymoron because the blockchain itself is highly centralized. This means that BSC validators aren’t rewarded with newly minted BNB for securing the network, but rather solely by racking up transaction fees. Unlike Ethereum, which is still a Proof-of-Work-based protocol, BSC uses a hybrid consensus algorithm called Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA), which allows BSC to achieve significantly higher transaction throughput without sacrificing security.Īnother critical difference between the two competing blockchains is that, unlike Ethereum, whose native token ETH is inflationary, BSC’s native token BNB is deflationary (burned by Binance on a regular schedule). That’s why we emphasized “DeFi” in the title– the Binance Smart Chain is centralized to Binance as a company.
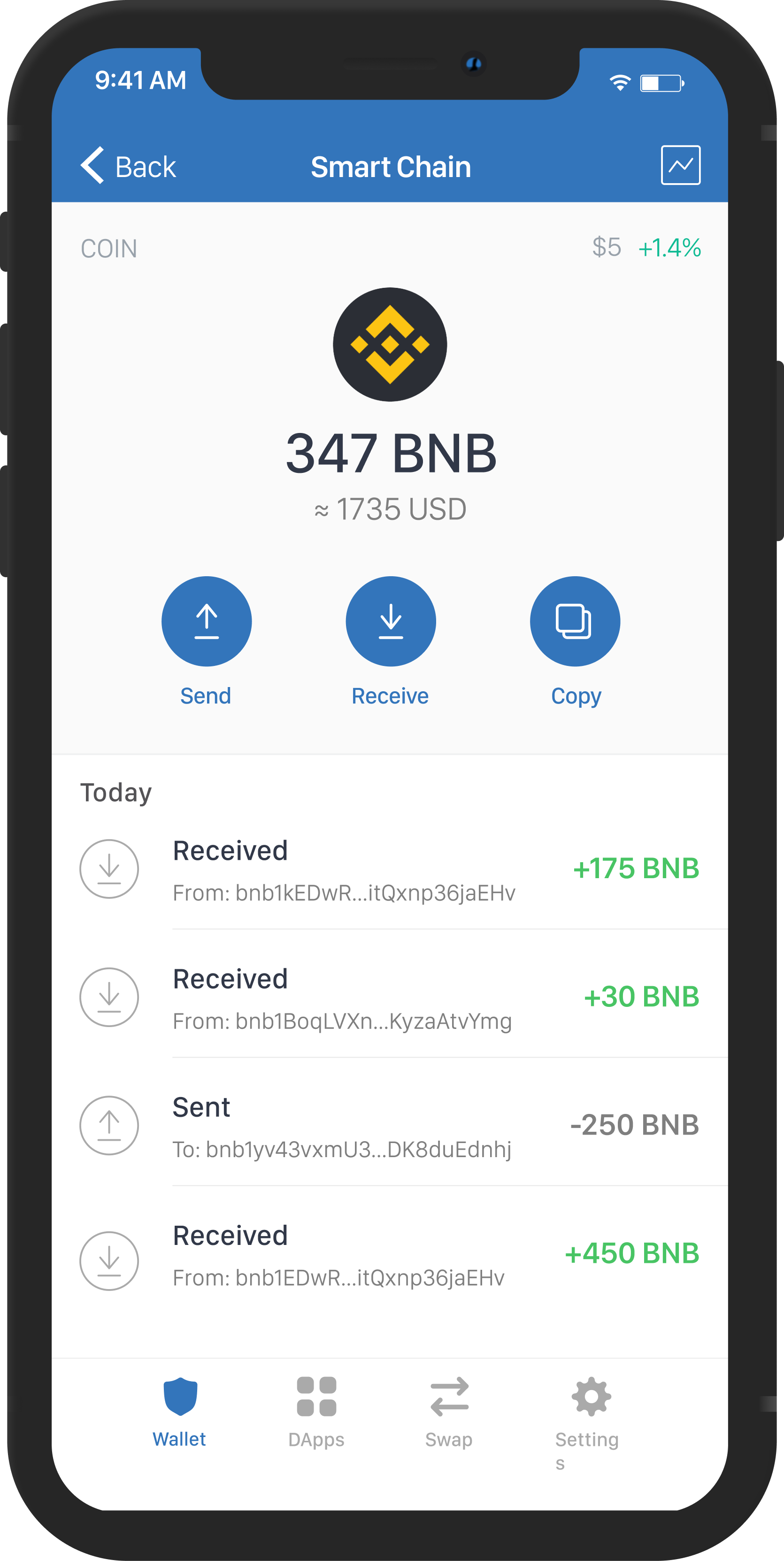
Instead, it is an entirely independent blockchain that operates side-by-side with the Binance Chain and supports smart contract functionalities and compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). It’s important to note, right out the gate, that the Binance Smart Chain is not an off-chain or layer-2 protocol running on top of the Binance Chain.
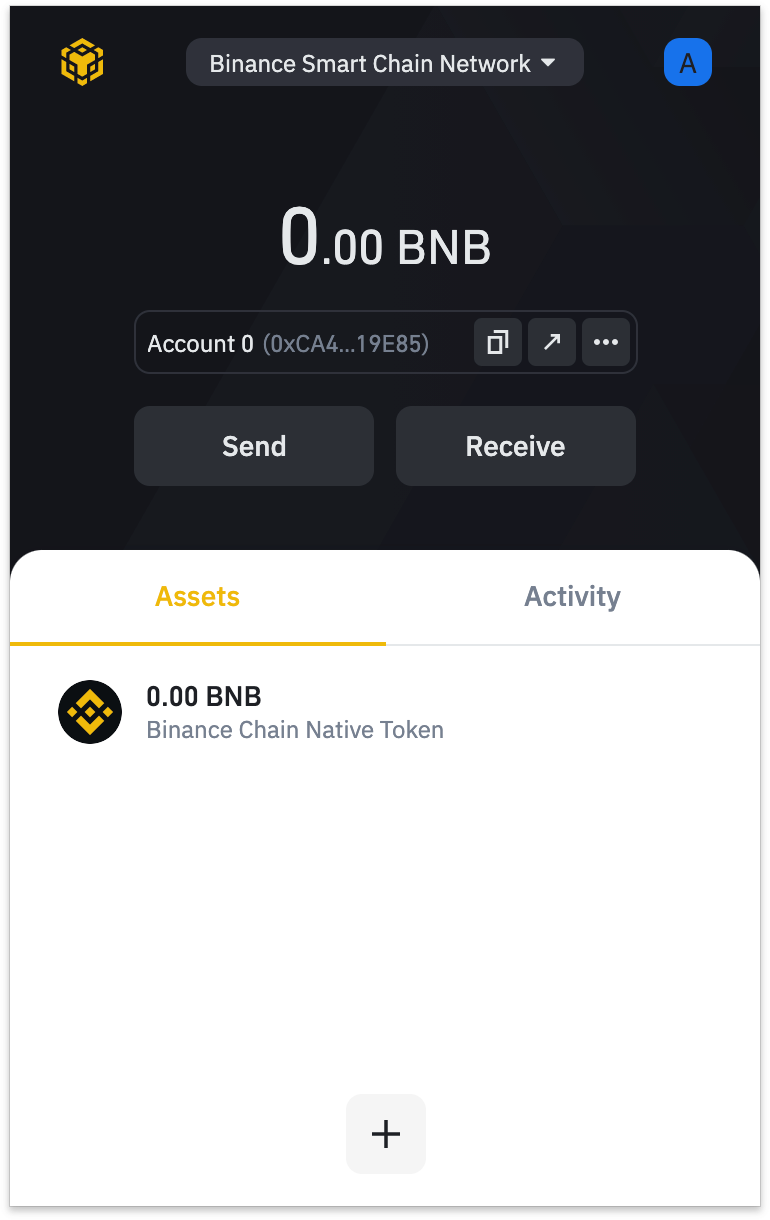
The Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is a blockchain protocol built by one of the largest centralized exchanges in crypto, Binance, that operates in parallel with the Binance Chain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
